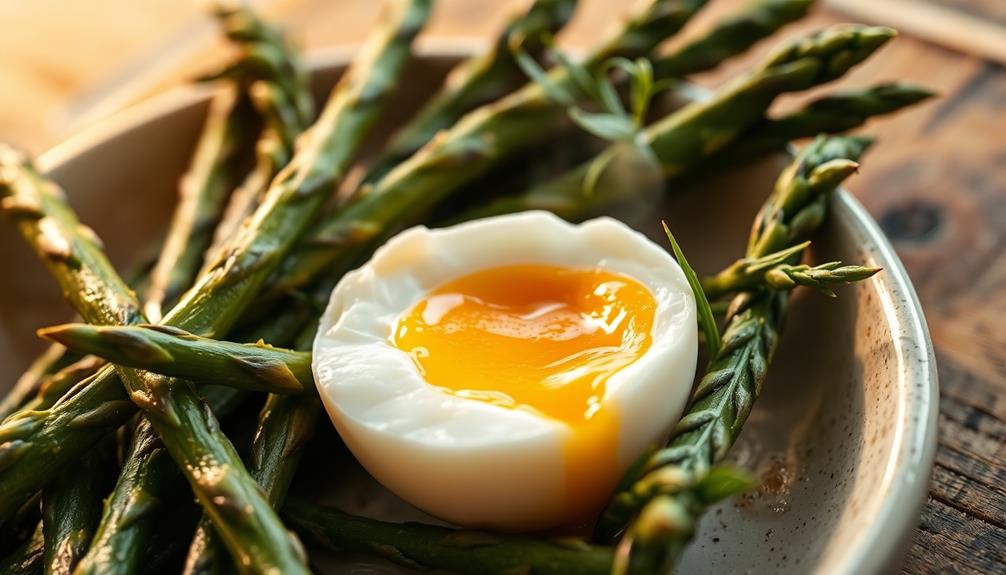
To achieve perfectly cooked eggs, you need to understand their composition and how heat impacts texture. Egg whites transform at about 180°F (82°C), while yolks offer essential fats and emulsifiers. For hard-boiled eggs, start with cold water and simmer for approximately 11 minutes, then cool them quickly in ice water to enhance peeling. Fresh eggs are tricky to peel due to their acidity, so opt for older eggs instead. Whether you boil or steam them, temperature control is key to avoiding rubbery whites. Want to explore more techniques and creative recipes? There's plenty more to discover!
Key Takeaways
- Cooking eggs at an ideal temperature of 180°F (82°C) ensures firm whites and prevents a rubbery texture.
- Fresh eggs have higher acidity, making them harder to peel; using older eggs simplifies peeling.
- Chilling hard-boiled eggs in ice water for 15 minutes halts cooking and improves peeling success.
- Steaming eggs is gentler than boiling, reducing cracking and yielding tender whites for optimal texture.
- Egg yolks contain lecithin, a powerful emulsifier, enhancing texture when used in sauces or dressings.
Understanding Egg Composition
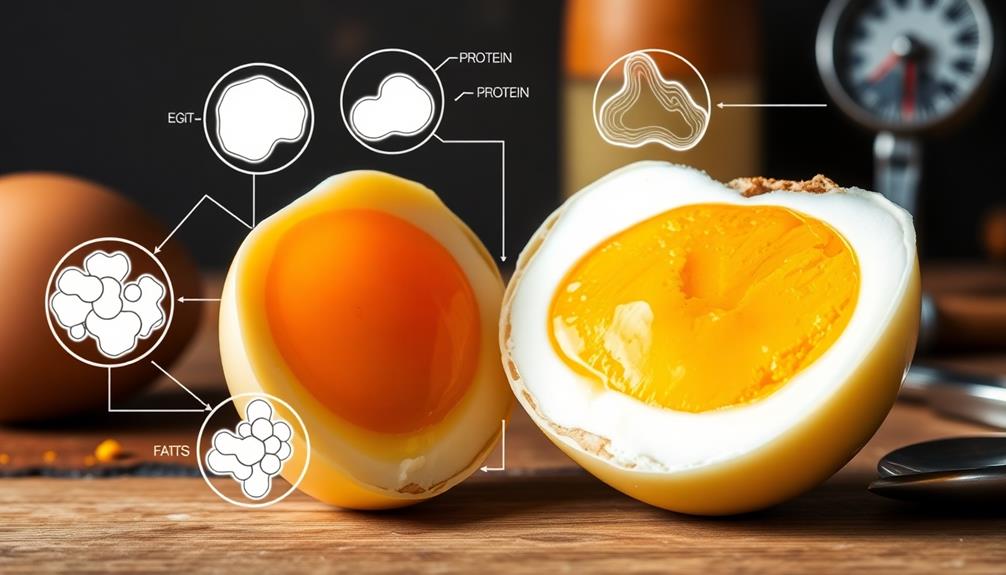
Understanding the composition of eggs is essential for perfect cooking results. Eggs consist of several key components: egg whites and egg yolks.
The egg whites, or albumen, make up about 67% of an egg's liquid weight and contain four distinct layers. The inner layers are thicker and protect the yolk, while the outer layers, which can become thinner as the egg ages, make peeling easier. Fresh egg whites have a pH of 7.6-7.9, which increases over time due to carbon dioxide loss. The versatility of eggs in dishes like Chinese steamed egg showcases their ability to shine in various culinary contexts.
On the other hand, egg yolks account for 33% of the egg's liquid weight. They're rich in fat and nearly half the protein content of the egg. These yolks also provide essential vitamins A, D, and E, contributing to their nutritional value. Notably, the pH of the yolk remains stable at around 6.0, which helps maintain its cooking properties as it ages.
Moreover, the eggshell, comprising 9-12% of the total weight, is primarily made of calcium carbonate and features thousands of pores for gas exchange.
Understanding these components will elevate your egg-cooking game considerably.
The Role of Heat in Cooking
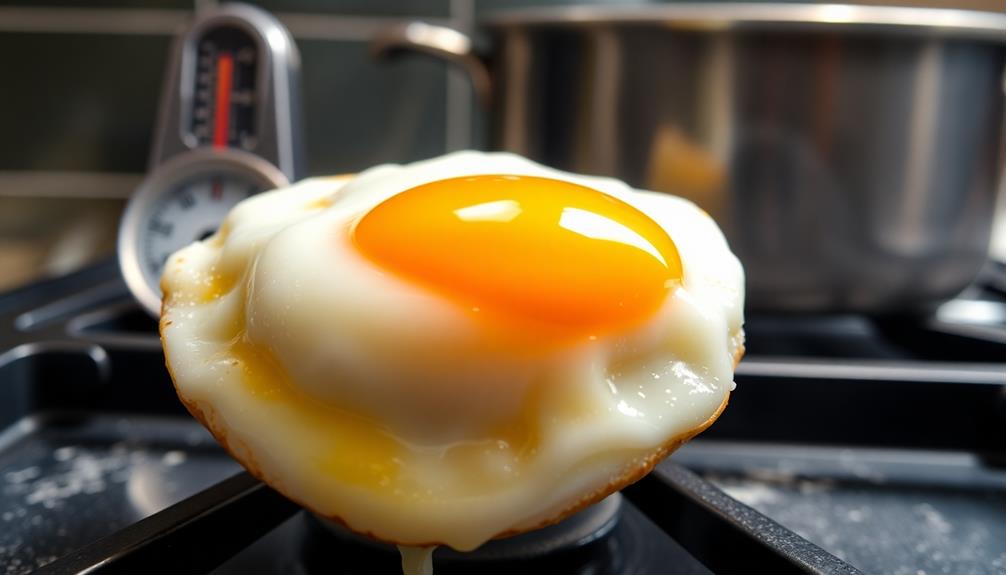

How does heat transform eggs from a liquid to a solid state? When you apply heat to eggs, it agitates the proteins in the egg whites. This agitation causes them to uncurl and form new connections, creating a firm structure as they cook.
For perfectly firm egg whites, you'll want to maintain an ideal cooking temperature of around 180°F (82°C). Additionally, cooking techniques can be enhanced with seasonal ingredients, such as in a Nettle and Potato Soup, where the freshness adds depth to the dish.
If the heat is too high, the proteins can over-bond, resulting in a rubbery texture that's far from desirable. Cooking egg whites at a lower temperature, like 170°F (77°C), yields pale yellow, crumbly whites. This highlights how essential temperature control is for achieving your desired texture.
As heat works its magic, the proteins capture surrounding water, leading to a solidified network that enhances both texture and moisture in the cooked eggs.
Techniques for Hard-Boiled Eggs
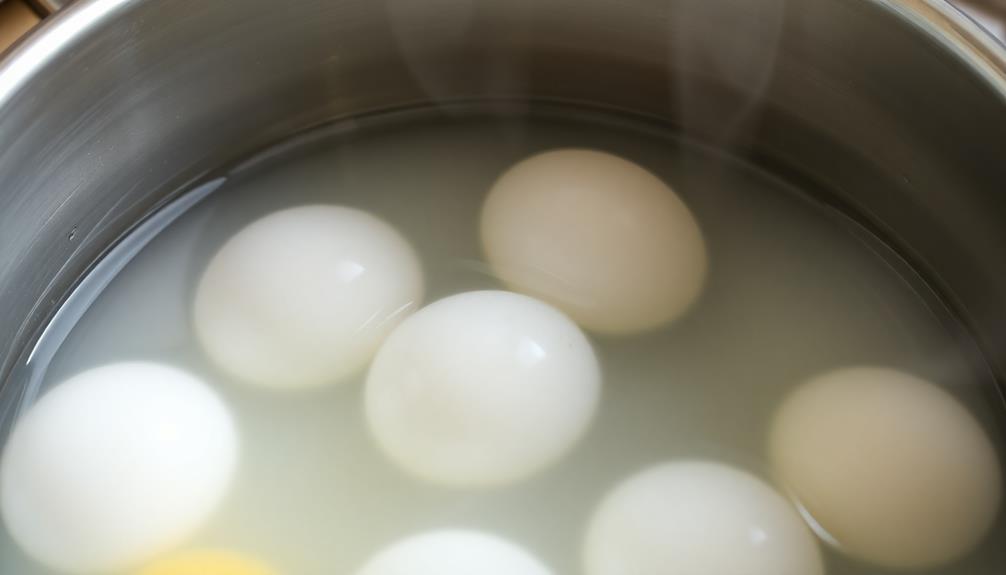

Cooking eggs to perfection requires attention not just to heat but also to technique, especially when it comes to hard-boiled eggs. For hard cooking, start by placing your eggs in a pot and covering them with cold water. Bring the water to a boil, then reduce the heat to a simmer. Cook your eggs for about 11 minutes for perfectly cooked hard-boiled eggs.
Using gentle methods is crucial, similar to the careful preparation of dishes like Caldeirada that require a delicate touch for superior flavor.
To guarantee the best texture, maintain a temperature around 180°F (82°C) while simmering. Boiling eggs directly can lead to rubbery egg proteins, so gentle methods are key.
After the cooking time is up, immediately transfer the eggs to a bowl of ice water. This chilling technique not only halts the cooking process, preventing overcooking, but it also helps with peeling later by firming the egg structure.
Keep in mind that fresh eggs can be trickier to peel due to their acidity. If you're using older eggs, peeling should be much easier.
Factors Affecting Egg Freshness
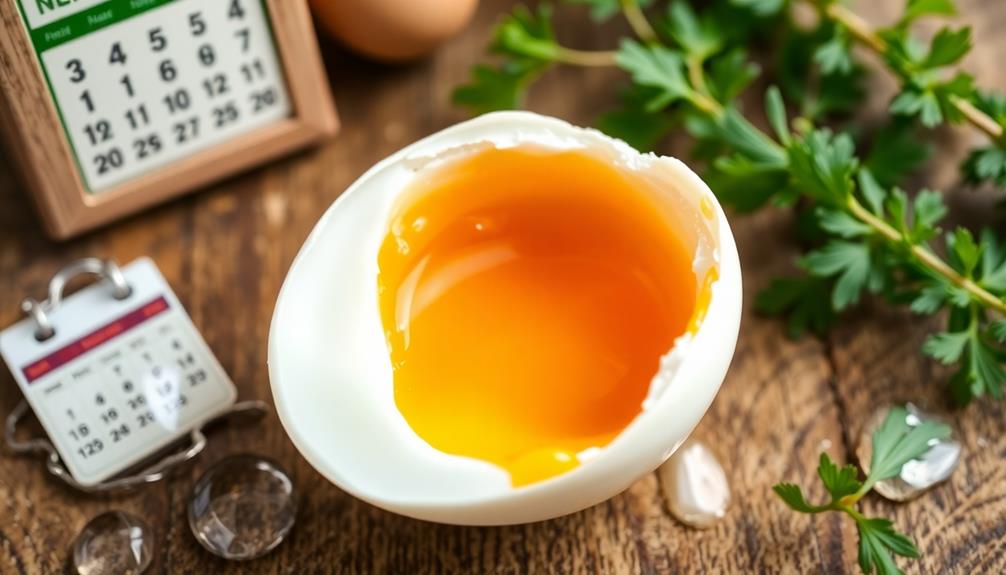

When you're cooking eggs, freshness plays a big role in how easily they peel. Fresh eggs can be tougher to work with due to their higher acidity, while older eggs tend to peel more easily.
Additionally, the cooking methods used can affect the final texture of the egg, making it essential to contemplate the nuances of different culinary traditions, such as Asian Cuisine.
Plus, where you store your eggs—whether at room temperature or in the fridge—can impact their aging process and overall quality.
Freshness and Cooking Difficulty
Understanding the freshness of eggs plays an essential role in achieving the perfect boil. When you boil eggs, the age of the egg can drastically impact not just the cooking process but also the peeling experience.
Fresh eggs have higher acidity levels due to trapped carbon dioxide, making them more challenging to peel post-boiling. On the other hand, older eggs are often easier to work with because they've larger air spaces, which reduce the shell's adherence to the egg white.
Just like ensuring the right spices for a flavorful dish, the right egg freshness can greatly enhance your cooking results.
Here are four key factors affecting egg freshness and cooking difficulty:
- Age: In the U.S., eggs can be up to 30 days old before packaging, affecting their acidity and peeling.
- Air Space: Aged eggs develop larger air pockets, facilitating easier peeling after boiling.
- Storage Conditions: Refrigerated eggs maintain quality for 4-5 weeks, while room temperature storage speeds up aging.
- Cooking Method: The boiling technique you use can further influence how easily the shell comes off.
Storage Temperature Impact
The way you store your eggs can greatly affect their freshness and cooking performance. When you leave eggs at room temperature, they age faster—one day on the counter equals about a week in the fridge! To maintain quality, refrigerate your eggs, as they stay fresh for 4-5 weeks post-packing date.
Cold storage slows down the aging process, which is essential for preserving their texture and cooking properties. Additionally, just like how traditional Ethiopian dishes emphasize fresh ingredients, using fresh eggs can considerably enhance the quality of your meals.
As eggs age, the pH of the egg whites increases due to the loss of carbon dioxide, leading to thinner whites that require lower temperatures for proper coagulation during cooking. Fresh eggs generally have a pH of 7.6-7.9, allowing for better structure and richer texture.
When you cook with older eggs, you may notice a decline in quality, impacting your final dish.
Best Practices for Peeling Eggs
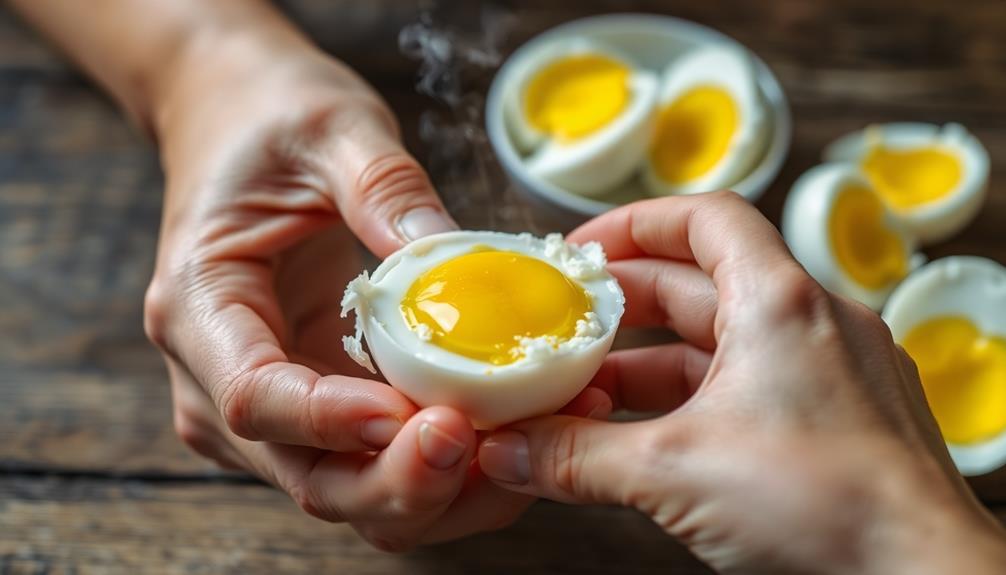

When it comes to peeling eggs, freshness plays an essential role in how easily the shell comes off. Older eggs tend to peel more easily than fresh ones because the pH level of the egg white increases over time, making it less likely to stick to the shell.
To improve your chances of a smooth peel, chill your hard-boiled eggs in ice water for at least 15 minutes after cooking. This simple step, along with using older eggs, can make a significant difference in achieving perfectly peeled eggs.
For instance, this technique can be particularly useful when preparing a Chefs Salad that requires beautifully sliced hard-boiled eggs to enhance its presentation.
Egg Freshness Impact
Peeling hard-boiled eggs can be a frustrating task, especially if you're working with fresh ones. Freshly laid eggs have higher acidity, causing them to cling to their shells, making peeling eggs a challenge.
To guarantee you get perfect boiled eggs, consider the impact of egg freshness and follow these best practices: Additionally, just as with traditional Italian dishes like Agnolotti, where the quality of ingredients matters, using older eggs will enhance your cooking experience.
- Use Older Eggs: Aim for eggs that are at least a week old. The aging process reduces the acidity of the egg whites as carbon dioxide escapes, making peeling much easier.
- Chill After Boiling: After boiling, immediately place the eggs in ice water for at least 15 minutes. This not only firms up the egg structure but also helps with loosening the shell.
- Peel Under Running Water: Try peeling your eggs under cool running water. This can help loosen the shell and make the peeling process smoother, especially for those fresher eggs.
- Crack and Roll: Gently crack the shell all around and roll the egg on the countertop. This can create small fractures that allow water to seep in, easing the shell's removal.
Chilling Techniques Importance
Chilling hard-boiled eggs right after cooking can make all the difference in peeling them effortlessly. When you plunge your cooked eggs into ice water for at least 15 minutes, you greatly improve the ease of peeling. This chilling process firms up the egg white structure, making it less likely to tear or stick to the shell.
For a festive touch, consider pairing your perfectly cooked eggs with a delicious Turkey Sandwich using leftover turkey from your Thanksgiving feast. If you're planning ahead, refrigerating your eggs overnight can further stabilize that structure, reducing the likelihood of poorly peeled eggs by about 50%.
The cold water not only halts the cooking process—preventing rubbery whites and green yolks—but also helps maintain a firm consistency that minimizes damage during peeling.
When it's time to peel, try doing it under cool running water. This technique can help loosen the shell, giving you a better chance of removing it without harming the delicate egg white.
With these chilling techniques, you'll find that enjoying perfectly cooked, beautifully peeled eggs is easier than ever. So, remember, a little chilling goes a long way in achieving egg-peeling perfection!
Cooking Methods: Boiling vs. Steaming
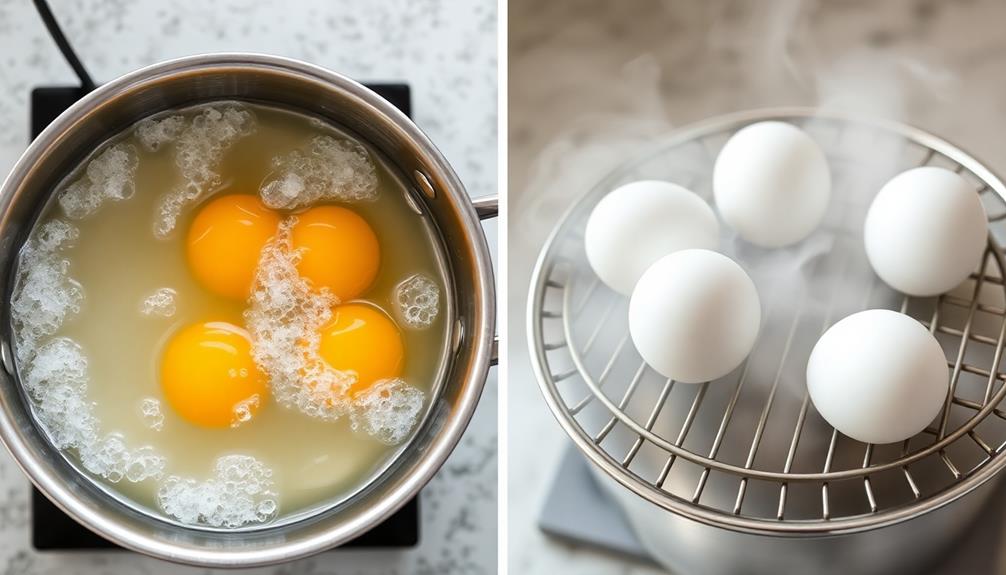

Boiling eggs and steaming them are two popular cooking methods, each with its own advantages. When you boil eggs, you start with boiling water and reduce the heat to a gentle simmer. However, boiling can lead to rubbery egg whites if the cooking temperature is too high.
On the other hand, steaming cooks eggs in a basket over boiling water, allowing for more controlled and even cooking. This method helps maintain a tender texture due to lower cooking temperatures. Notably, the delicate balance of cooking techniques can be likened to the precision required in preparing traditional Japanese dishes like Dorayaki (Red Bean Pancake), where the right temperature and timing are vital for achieving the desired fluffiness.
Here are key points to reflect upon when choosing between boiling and steaming:
- Cooking Temperature: Steaming allows you to achieve the ideal cooking temperature of around 180°F (82°C) more easily than boiling.
- Cracking Prevention: Steaming reduces the chances of cracking eggshells by providing gentle heat and gradual temperature changes.
- Timing: For hard-boiled eggs, boiling typically takes about 11 minutes, while steaming might take slightly less time due to efficient heat transfer.
- Texture Control: Steaming results in softer egg whites, making it ideal if you prefer a tender bite.
The Science of Egg Emulsification
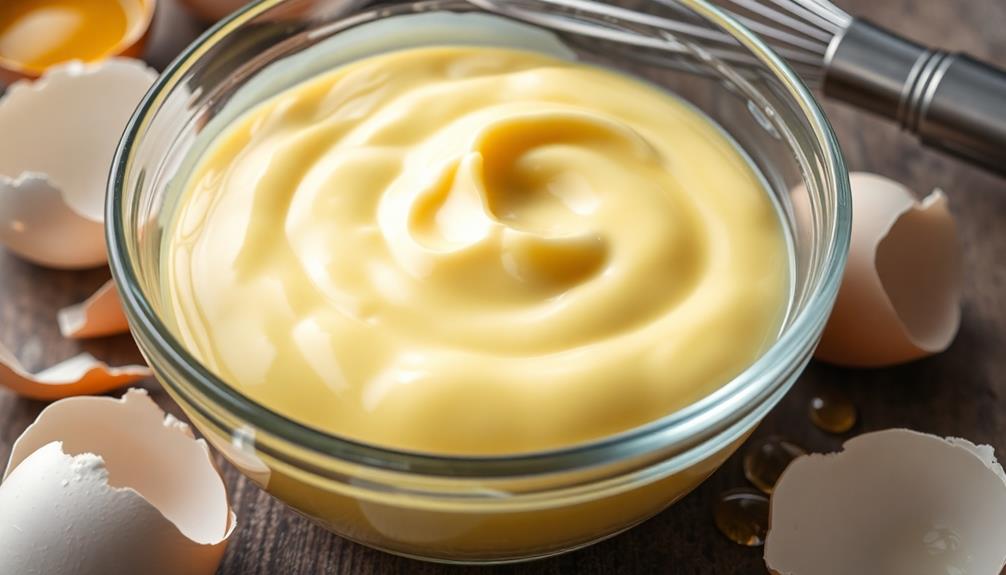

Emulsification is a fascinating process that plays an essential role in many culinary applications, particularly in creating stable sauces like mayonnaise and hollandaise. At the heart of this process are egg yolks, which contain lecithin, a powerful emulsifier. This phospholipid helps form stable oil-in-water emulsions by allowing the mixture of oil and water to blend seamlessly.
When you whisk egg yolks into fat, the mechanical action incorporates air, creating a homogeneous mixture. The unique properties of egg proteins come into play here; they possess both water-attracting (hydrophilic) and water-repelling (hydrophobic) characteristics. This dual nature enables them to bond with both oil and water, effectively stabilizing the emulsion and preventing the oil droplets from coalescing.
Temperature also impacts the effectiveness of emulsification. Using room temperature eggs enhances their emulsifying properties, while cold eggs may hinder the process.
Understanding how egg yolks act as emulsifiers can greatly affect the texture and consistency of your sauces, making it vital for your culinary success. So, next time you whip up a sauce, remember the science behind those egg yolks!
Creative Egg Recipes
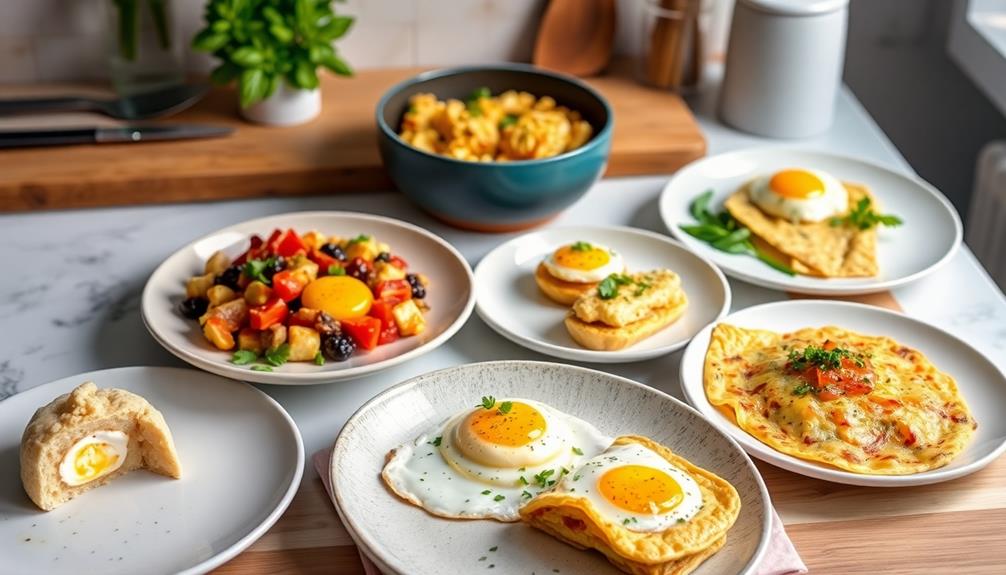

Exploring the versatility of eggs opens up a world of creative culinary possibilities.
Whether you're looking to elevate your brunch or use up those leftover Easter eggs, there are plenty of delicious options to try. Here are four ideas to inspire your next meal:
- Deviled Eggs: Give the classic deviled egg a modern twist by mixing in creamy avocado or a kick of sriracha. This not only enhances the flavor but also adds a unique texture.
- Marinated Soft-Boiled Eggs: Soak your cooked eggs in a mixture of soy sauce, mirin, and sesame oil for several hours. This creates rich, flavorful marinated soft-boiled eggs perfect for ramen.
- Egg Salad Sandwiches: Mix boiled eggs with fresh herbs like dill or tarragon, and add a touch of mustard or Greek yogurt for a tangy, invigorating filling in your sandwiches.
- Sous Vide Eggs: Cook eggs at 63°C (145°F) for 45 minutes to achieve a custard-like texture that can elevate any dish.
With these creative uses for eggs, you'll never run out of tasty ideas!
Troubleshooting Egg Cooking Issues
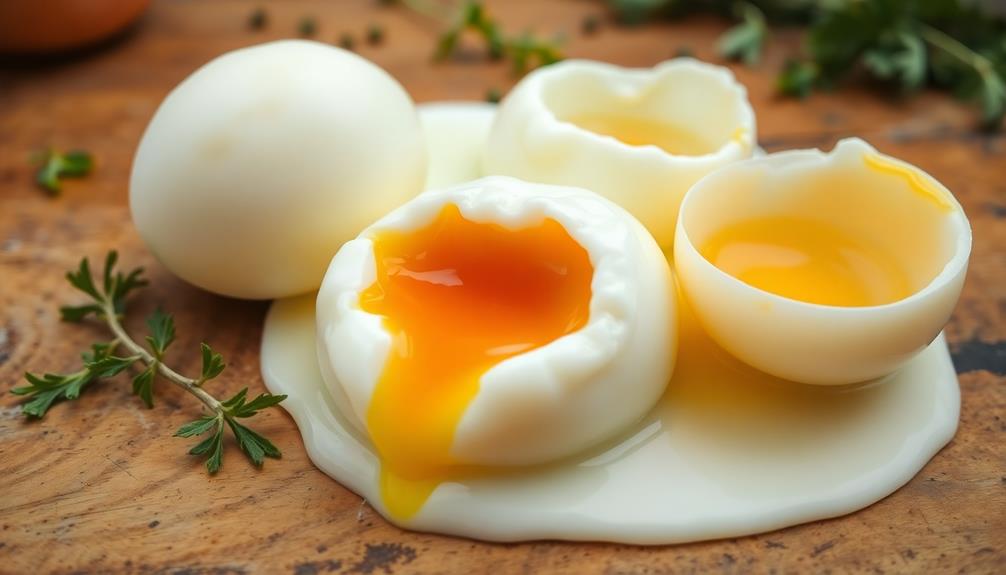

When it comes to cooking eggs, even the simplest methods can sometimes lead to unexpected issues. If you find your boiled eggs difficult to peel, try using older eggs. Their higher pH makes peeling easier.
To avoid rubbery egg whites, keep a close eye on your cooking temperature; aim for around 180°F (82°C) for firm whites and steer clear of boiling over 212°F (100°C) to prevent overcooking.
If you notice green rings around the yolk, that's a sign you've overcooked them. Quick cooling in ice water can halt the cooking process and minimize those unsightly rings.
For consistently tender egg whites, consider gentle cooking methods like steaming or starting with cold water to allow for slow, controlled heating.
Lastly, handle fresh eggs with care. Cracking them before boiling can lead to messy leaks. If you're worried about cracks forming during cooking, adding a bit of salt to the water can help seal any small fissures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Science Behind Cooking Eggs?
When you cook eggs, heat denatures proteins, causing them to unfold and solidify. The cooking method and temperature greatly influence texture; lower temperatures yield tenderness, while higher ones create rubbery, overcooked results you'll want to avoid.
How Do You Make Perfectly Cooked Eggs?
To make perfectly cooked eggs, start with cold eggs in boiling water. Cook for 11 minutes, then chill in ice water. Experiment with times and methods to find your ideal yolk consistency and texture.
What Is the Chemistry Behind Boiled Eggs?
Think of boiling eggs like a delicate dance; the proteins twist and turn with heat. As you cook, temperatures dictate textures—too high, and you end up with rubbery whites. Timing's everything for that perfect bite!
What Is the Science Behind Soft Boiled Eggs?
When you soft boil eggs, you control the cooking time and temperature. Keeping them around 170°F to 180°F lets the whites set while the yolk stays runny. Quick chilling prevents overcooking and that green ring.
Conclusion
To sum up, mastering the art of cooking eggs not only enhances your culinary skills but also opens up a world of delicious possibilities. Did you know that the average American consumes about 279 eggs per year? With this knowledge, you can elevate your egg game, whether you're whipping up a classic omelet or perfecting hard-boiled eggs. So, embrace the science behind egg cooking and enjoy the incredible versatility they offer in your kitchen!









