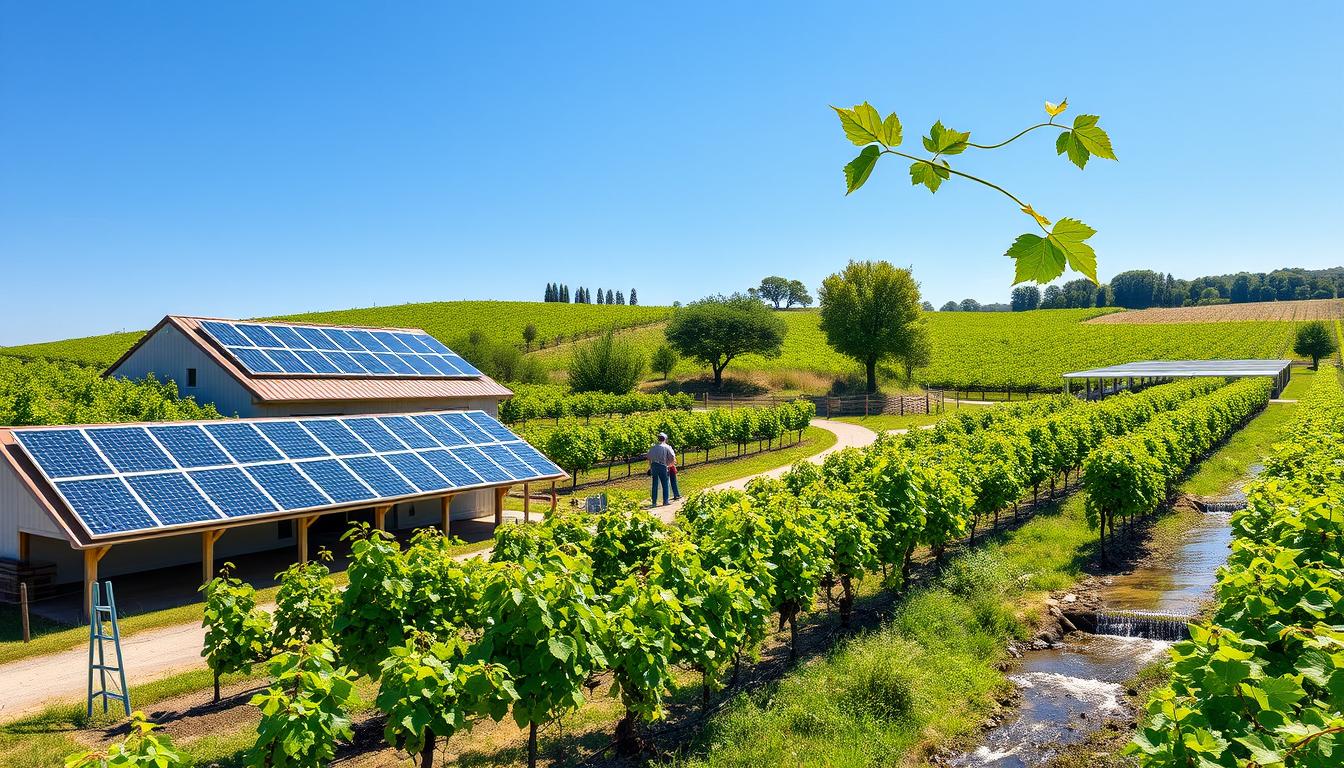
Imagine standing in a sun-drenched vineyard, the air filled with the sweet scent of ripening grapes. You might find solace in knowing that the wine you enjoy not only delights your palate but also nurtures the land it comes from. In today’s world, where 98% of consumers are increasingly drawn to eco-friendly and sustainable wine brands, the impact of your choices has never been more significant. Addressing climate challenges and promoting responsible practices, sustainable vineyards prioritize the earth’s health alongside the art of winemaking. With distinguished locations like Sonoma County in California leading the way, wineries globally are embracing eco-friendly methods that safeguard their natural resources for future generations.
From the biodynamic practices pioneered by Château Pontet-Canet in Bordeaux to the organic approaches at Emiliana Organic Vineyards in Chile, winemakers are weaving sustainability into their very fabric. Not only do these practices protect the environment, but they also enhance the flavors and quality of the wines you cherish. As the wine industry becomes a beacon of sustainable agriculture, understanding the values behind these methods can help you make informed decisions and connect more deeply with the world of wine.
Key Takeaways
- 98% of consumers are now more interested in eco-friendly and sustainable wine brands.
- Sustainable vineyards prioritize environmental stewardship alongside quality winemaking.
- Biodynamic practices have gained traction in renowned regions like Bordeaux and Montepulciano.
- Innovative methods in sustainable viticulture improve both wine quality and ecosystem health.
- Embracing sustainability in winemaking leads to long-term economic viability and community benefits.
Understanding Sustainable Winemaking
Sustainable winemaking represents a proactive approach to producing wine with care for the environment, the community, and the overall quality of the product. By prioritizing eco-friendly practices, wineries can ensure that they contribute positively to the ecosystem while maintaining high production standards. This section delves into what defines sustainable wine and the various benefits of choosing these exceptional offerings.
What Defines Sustainable Wine?
Sustainable wine is characterized by a commitment to environmentally sound, economically viable, and socially equitable practices throughout the entire winemaking process. These wines avoid the use of harmful chemicals, fostering soil health and promoting biodiversity. Several certifying bodies around the world provide certifications that validate the authenticity of sustainable wines, assessing farms based on their responsible farming methods, energy efficiency, and adherence to ethical labor practices. This multifaceted approach helps ensure that your choice of wine contributes to a better future.
Benefits of Choosing Sustainable Wines
- Flavorful Experience: Sustainable wines often deliver superior taste, with organic and biodynamic varieties exhibiting complex flavor profiles that reflect the unique terroir of their growing regions.
- Worker Support: Many sustainable wineries prioritize fair wages and ethical treatment for their workers, directly contributing to local communities and economies.
- Environmental Conservation: Engaging in eco-friendly practices helps promote biodiversity, conserve water resources, and reduce chemical inputs, ensuring healthier ecosystems for future generations.
- Quality Assurance: Certified sustainable wines must meet strict guidelines, providing consumers with reassurance that their choices support sustainability.
- Social Responsibility: By selecting sustainable wines, you endorse companies that are committed to ethical practices and community well-being.

In summary, the benefits of sustainable wines extend beyond taste. They align with a growing trend that seeks to balance high-quality production with responsible environmental stewardship. By choosing sustainable wine, you actively support practices that contribute to a healthier planet and society.
Overview of Sustainable Vineyards
Sustainable vineyards are at the forefront of modern agriculture, driving a movement that prioritizes eco-friendly practices while ensuring high-quality wine production. The principles of sustainable vineyard management are crafted to not only enhance the quality of the grapes but also to respect and protect the surrounding environment. This commitment strengthens the ecosystem and creates a positive ripple effect on biodiversity in wine production.
Principles of Sustainable Vineyard Management
At the heart of sustainable vineyard management lies a combination of responsible farming practices. These include:
- Utilization of natural ground cover to improve soil health and moisture retention.
- Minimization of chemical pesticides and fertilizers, prioritizing worker and consumer safety.
- Implementation of water and energy conservation methods, significantly reducing resource use.
- Engagement in third-party certification programs such as SIP and CSWA, ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Impact on Environment and Biodiversity
The environmental impact of vineyards extends far beyond the boundaries of traditional farming methods. Sustainable vineyards nurture biodiversity while maintaining ecological balance. By enhancing habitats for beneficial wildlife, farmers naturally control pests without relying on harmful insecticides. Practices like compost application and careful water management contribute to healthy soil ecosystems, all while supporting the vast array of life that operates within vineyard landscapes.
The Role of Eco-Friendly Wineries
Eco-friendly wineries play a vital role in the wine industry, showcasing sustainable winemaking techniques that not only benefit the environment but also enhance the quality of the wines produced. These practices incorporate innovative solutions to reduce environmental impact while promoting resource efficiency. Below are some notable techniques employed in these wineries:
Techniques Used in Eco-Friendly Winemaking
- Organic Vineyard Practices: Utilizing organic methods helps eliminate synthetic chemicals, fostering a balanced ecosystem.
- Biodynamic Farming: This approach enhances vineyard vitality by aligning agricultural activities with celestial cycles, yielding unique grape flavors.
- Water Conservation Strategies: Efficient water management is crucial in sustainable wine growing, significantly minimizing waste.
- Energy-Efficient Machinery: Adoption of energy-saving tools and systems reduces overall energy consumption.
- Sustainable Packaging: Eco-friendly packaging solutions help decrease the carbon footprint associated with wine distribution.
Certifications for Sustainable Wineries
Certifications for sustainability serve as a benchmark for eco-friendly wineries, ensuring they adhere to rigorous standards in their practices. Some prominent certifications include:
- Organic Certification: Guarantees adherence to environmentally friendly practices, avoiding synthetic chemicals and harmful pesticides.
- Biodynamic Certification: Highlights the alignment with lunar cycles and emphasizes natural composting practices.
- Sustainable Winegrowing Certifications: Cover comprehensive sustainability principles, promoting holistic farming approaches.
These certifications not only validate the wineries’ commitment to sustainability but also build consumer trust. Eco-friendly wineries like Napa Valley’s Grgich Hills Estate and Italy’s Cantina Endrizzi exemplify commitment to these standards, showcasing their dedication to fostering a healthier planet through sustainable practices.

Sustainable Viticulture Practices
Sustainable viticulture emphasizes practices that maintain ecological balance while producing high-quality wine. This approach favors organic methods over conventional practices, resulting in healthier vineyards and superior flavor profiles. Understanding the differences between organic vs conventional wine reveals a significant impact on both the environment and the quality of grapes.
Organic vs. Conventional Practices
Organic viticulture stands as a cornerstone of sustainable wine production. It involves the elimination of synthetic chemicals, focusing instead on nurturing the ecosystem through natural methods. Here are some key aspects distinguishing organic from conventional practices:
- Organic vineyards avoid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
- Conventional methods may utilize chemicals that can harm soil health and biodiversity.
- Organic certification requires adherence to strict regulations and annual audits to maintain standards.
- Consumer demand for organic wines encourages more vineyards to adopt these sustainable viticulture practices.
Natural Grape Cultivation Methods
Natural grape cultivation methods enhance both the environment and wine quality. Various strategies are employed among vineyards to ensure sustainability while producing exceptional grapes:
- Implementing water management techniques, such as drip irrigation, minimizes water waste.
- Rainwater harvesting and recycling efforts contribute to reduced overall water consumption.
- Cultivating cover crops enriches biodiversity and improves soil health.
- Utilizing solar and wind energy reduces the carbon footprint associated with viticulture operations.
- Engaging with the local community through educational programs fosters shared commitment to sustainable practices.
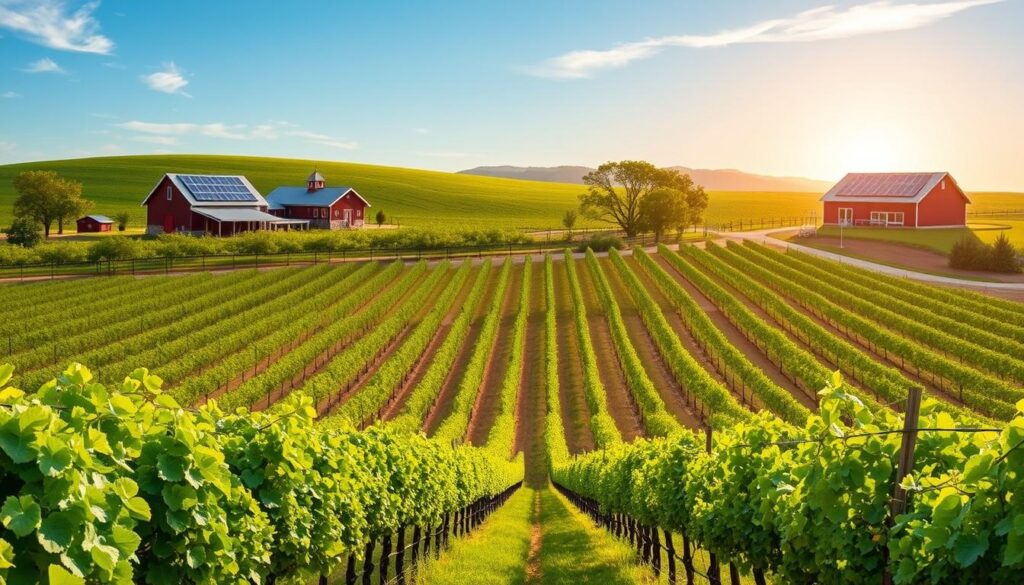

| Practice | Impact |
|---|---|
| Organic Certification | Enhances soil health, reduces chemical usage |
| Water Management | Minimizes waste, conserves resources |
| Biodiversity Enhancement | Supports ecosystem stability, improves grape quality |
| Community Engagement | Educates consumers, builds local support |
| Renewable Energy Use | Decreases carbon emissions, sustains vineyard operations |
Through the adoption of these natural grape cultivation methods, vineyards are not only able to produce better wine but also contribute positively to their surroundings. The ongoing shift towards sustainable viticulture practices reflects a growing recognition of the need to balance agricultural productivity with environmental health. By implementing these sustainable viticulture practices, vineyards are able to preserve the biodiversity of the surrounding ecosystems and minimize the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers. This not only benefits the local flora and fauna but also creates a more harmonious vineyard life, where natural processes are allowed to thrive. Ultimately, the adoption of these methods leads to a healthier, more resilient vineyard ecosystem and higher quality grapes for winemaking.
Green Viticulture Practices in Wine Production
Implementing green viticulture practices stands at the forefront of sustainable winemaking, offering avenues for responsible farming while boosting environmental health. As the industry faces challenges like climate change and resource scarcity, shifts towards effective water conservation in vineyards have become crucial. Such strategies not only help in mitigating drought conditions but also enhance grape quality, resulting in superior wines.
Effective Water Conservation Strategies
Water conservation in vineyards has gained increasing importance, especially in regions prone to water scarcity. Techniques such as:
- Drip Irrigation: Delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Captures and stores rainwater for irrigation, reducing dependency on groundwater.
- Cover Cropping: Helps improve soil structure and moisture retention, thereby further conserving water.
These methods not only promote sustainable practices but significantly reduce the vineyard’s overall environmental footprint.
Reducing Chemical Inputs and Enhancing Soil Health
Reducing chemical inputs plays a pivotal role in promoting a healthier vineyard ecosystem. Sustainable wineries are increasingly focusing on natural amendments and organic practices. By improving soil health through:
- Composting: Utilizes organic waste to enrich soil and enhances microbial activity.
- Cover Crops: Protect soil from erosion while providing nutrients naturally.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Employs beneficial insects and natural repellents to minimize pesticide use.
These practices contribute to robust vine growth, enhanced taste profiles, and ultimately superior wine production. A shift towards a reduced reliance on chemicals not only benefits the environment but aligns with the preferences of an increasing number of consumers seeking eco-friendly wines.
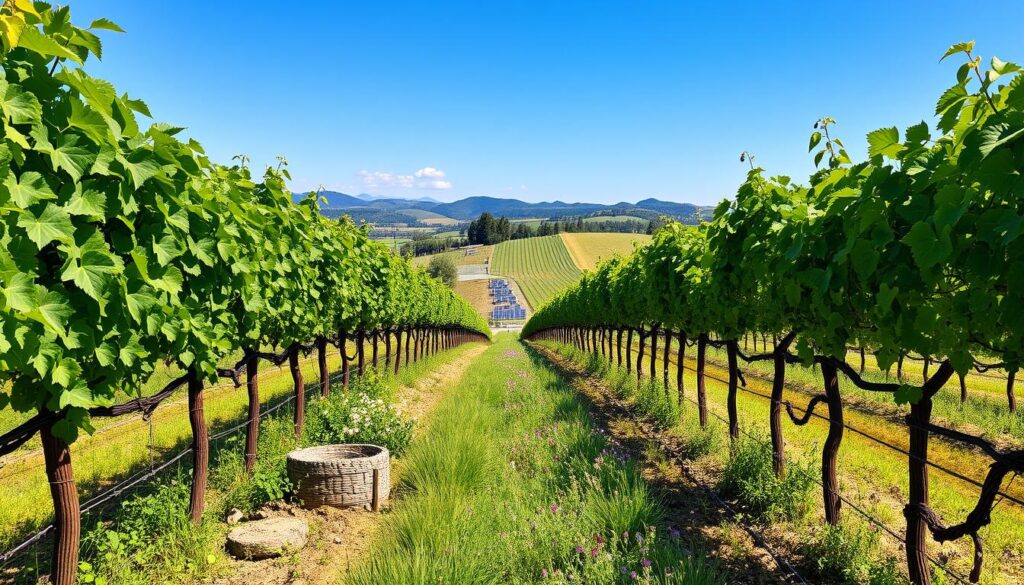

| Water Conservation Techniques | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Drip Irrigation | Water is delivered directly to the roots | Minimizes waste, maximizes efficiency |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Collecting and storing rainwater for irrigation | Reduces dependency on groundwater |
| Cover Cropping | Planting crops to protect soil | Improves soil structure and moisture retention |
The Importance of Regenerative Agriculture in Wine
Regenerative agriculture in wine harnesses nature’s ability to restore and enhance ecosystems. This dynamic approach focuses on rebuilding soil health, promoting biodiversity, and fostering water retention. Such methods play a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems, ensuring that winemaking supports not just the vineyard but the broader environment.
Maintaining Healthy Ecosystems
Through regenerative practices, vineyards can create a resilient ecosystem that flourishes over time. For instance:
- Integrating livestock allows for natural grazing, effectively managing weeds while enriching the soil.
- Utilizing cover crops sequesters carbon, improves soil fertility, and boosts biodiversity.
- Minimizing tillage practices helps preserve soil structure, reducing erosion and enhancing water retention.
- Leaving sections of land unfarmed supports local wildlife, contributing to ecological balance.
Examples of Successful Regenerative Practices
Several vineyards are leading the way with successful regenerative practices in vineyards:
| Vineyard | Practices Implemented | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Eco Terreno | Integrating livestock, seeding cover crops, using compost, low tillage | Enhanced soil health, reduced chemical use, increased biodiversity |
| Gamble Family Vineyards | Practicing regenerative agriculture since the 1960s | Improved fruity expression and complexity in wines |
| Tablas Creek Vineyard | Certified by the Regenerative Organic Alliance | Standards for animal welfare and sustainability |

These examples illustrate not only the powerful effects of regenerative agriculture in wine but also the dedication to maintaining healthy ecosystems for future generations. By adopting these successful regenerative practices, vineyards can positively influence the quality of their wines while nurturing their local environments.
How Sustainable Farming Benefits Vineyards
Sustainable farming plays a crucial role in the success of vineyards, directly influencing both the quality of wine and the resilience of local communities. By employing eco-friendly practices, vineyards can achieve numerous benefits while enhancing wine flavor profiles. Sustainable approaches focus on maintaining healthy soil and biodiversity, which greatly impacts grape quality and vinification.
Enhancing Flavor Profiles and Wine Quality
Utilizing natural methods, such as cover crops and integrated pest management, promotes biodiversity and ecological balance. Vineyards like Sebastiani use natural pest control through beneficial insects instead of pesticides, leading to healthier grapes. These practices support the characteristic terroir and elevate the sensory experience of wines, effectively enhancing wine flavor profiles. This focus on quality resonates with increasingly environmentally-conscious consumers, who appreciate wine made sustainably.
Long-term Economic Viability and Community Engagement
The benefits of sustainable farming for vineyards extend beyond wine quality. By aligning farming practices with economic and environmental goals, vineyards ensure their long-term viability. Sustainable practices like water conservation and reduced carbon emissions have proven effective. For instance, Ferrari-Carano reduces water usage by 30% through innovative irrigation techniques. Additionally, creating a sense of community engagement in winemaking leads to fair labor practices and supports local economies. What’s more, 85% of consumers show a willingness to pay a premium for sustainable wines, reflecting the increasing demand for ethical production.

| Key Benefits | Details |
|---|---|
| Wine Quality | Enhances flavor profiles through natural pest control and healthy soil management. |
| Water Conservation | Reduced water usage by implementing advanced irrigation systems. |
| Community Engagement | Involves locals in winemaking, ensuring fair labor practices. |
| Market Demand | Growing consumer willingness to pay premiums for sustainable wines. |
| Carbon Footprint | Reduction of carbon emissions through energy-efficient practices and waste management. |
The Future of Sustainable Vineyards
The future of sustainable vineyards appears promising, driven by a strong commitment to environmental stewardship and innovative approaches in winemaking. Understanding the direction of this sector involves exploring the latest trends and technological advancements that redefine eco-friendly practices.
Emerging Trends in Eco-Friendly Winemaking
Many wineries are embracing trends in eco-friendly winemaking that prioritize sustainable practices. Key developments include:
- Utilizing natural fertilizers and pest control methods instead of chemical options.
- Enhancing biodiversity through the implementation of cover crops and reduced tilling.
- Adopting water management techniques such as drip irrigation and soil moisture monitoring to optimize water usage.
- Integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to reduce carbon emissions.
- Promoting community involvement by supporting local charities and educating consumers on the importance of sustainability.
Technological Innovations Supporting Sustainability
Technological innovations in winemaking are transforming the future of sustainable vineyards. These advancements play a vital role in enhancing production efficiency while minimizing environmental impact:
- Digital marketing strategies are helping wineries connect with consumers, educating them on sustainability practices.
- Waste utilization techniques allow wineries to repurpose by-products, contributing to a circular economy.
- Adopting lightweight bottling and eco-friendly packaging has significantly decreased carbon footprints across the supply chain.

Conclusion
The journey towards eco-friendly winemaking with sustainable vineyards is essential not only for our planet’s health but also for enriching your wine experience. By choosing sustainable options, you indulge in high-quality wines while supporting practices that enhance environmental protection and community well-being. Sustainable wine production utilizes environmentally friendly practices from vineyard management to bottling, ensuring that each bottle represents a responsible choice.
As more wineries adopt organic farming methods, they avoid synthetic chemicals in favor of natural alternatives like composting and biological pest control. This shift not only mitigates environmental impact but also leads to healthier vines and superior grapes. Furthermore, sustainable wineries are implementing water-saving techniques, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, allowing for effective resource management in the face of climate change challenges.
With growing consumer awareness, the shift towards sustainable wine production transforms from a trend into a necessary movement within the industry. By embracing these eco-friendly practices, you contribute to a thriving ecosystem that celebrates not just taste but also a commitment to the planet and future generations. Ultimately, the benefits of sustainable farming resonate far beyond the vineyard, fostering a culture of responsibility and excellence in winemaking.








